How many industrial manufacturing steps are required to produce a control arm?
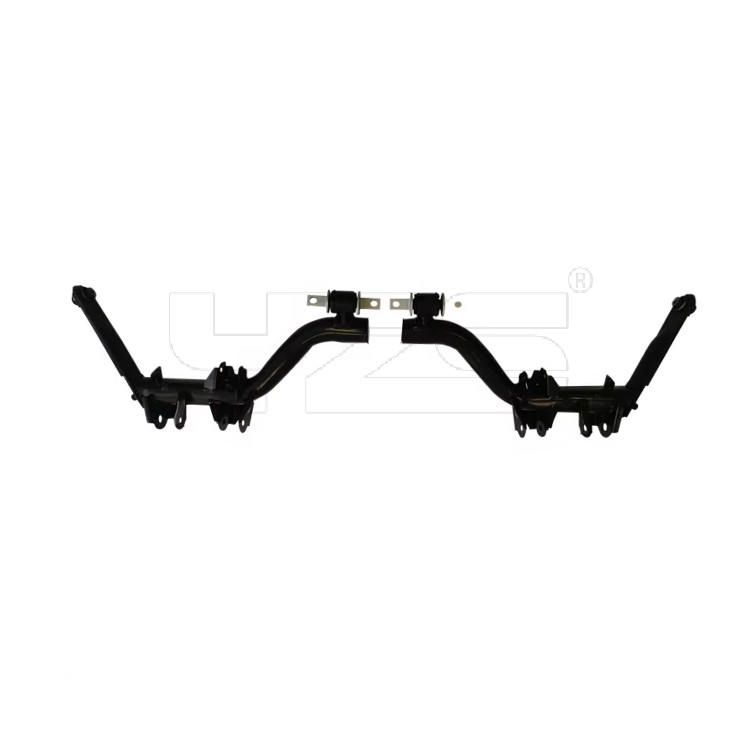

1. Stamped Steel Control Arm (Most Common for Mass Production)
This is the most common method for standard passenger vehicles, prioritizing cost-effectiveness and high volume.
1. Blank Cutting: Coiled sheet steel is cut into specific-sized blanks.
2. Stamping/Forming: The blanks are placed in a large stamping press and formed into the control arm's half-shell shape using massive dies. This often requires multiple progressive dies.
3. Trimming & Piercing: Excess material (flash) is cut away, and necessary mounting holes are punched out.
4. Robotic Welding: Since stamped arms are typically made of two halves, robotic welding is used to join them into a complete unit. The bushings sleeves may also be welded in at this stage.
2. Cast or Forged Control Arm (For High Strength & Performance)
Casting:
Process: Molten metal (typically cast iron or aluminum) is poured into a mold. This is ideal for complex, 3D geometries.
Advantage: Design freedom, excellent for integrating strength ribs and complex shapes.
Post-Process: The cast part must be cleaned (removing gates and risers) and often undergoes heat treatment.
Forging:
Process: A solid billet of metal (usually aluminum or steel) is shaped under extremely high pressure, creating a superior grain flow.
Advantage: Highest strength-to-weight ratio, excellent durability. Used for performance and heavy-duty applications.
Post-Process: Requires heat treatment and extensive machining.
3. Common Secondary Processes
Regardless of the primary method, the following steps are almost always required:
5. Heat Treatment: Processes like quenching and tempering are used to achieve the required strength, hardness, and durability. This is critical for cast and forged arms.
6. Machining (CNC): This is a critical step for precision. CNC machines are used to create accurate mounting points for the ball joint, bushings, and other pivot points, ensuring perfect dimensions and alignment.
7. Joining: While welding is specific to stamped arms, other methods like pressing are used for all types.
8. Surface Treatment: To prevent corrosion, a coating is applied. Common methods include:
E-coating (Electrophoretic Coating): The most common and effective method for corrosion resistance.
Powder Coating: Provides a thicker, more durable, and aesthetically pleasing finish.
9. Assembly: Bushings (rubber or polyurethane) are pressed into their housings. The ball joint is either pressed in, bolted on, or integrated during forging/casting.
10. Quality Control: This is continuous and includes dimensional checks, material testing, hardness testing, non-destructive testing like Magnetic Particle Inspection or X-ray (for castings/forgings), and functional tests.
Summary
Contact Person
- Name:
- Jessica
- Tel:
+0086-576-87221128
+0086-13736677602
- WhatsApp:
- 8613736677602
- Address:
- Building 62, Chuangrong Industrial Zone, Yucheng Street, Yuhuan, Zhejiang 317600
subscription
Signup for our newsletter to stay up-to-date on our promotions, discounts, sales, special offers and more
 +
+
